Capacitor Color Coding
Capacitor Number Coding Chart
By referring to the above table, one can acknowledge the value
of the capacitor, easily. Follow the below example for a better understanding.
In the below example, the first two digits represent the first and the second
significant digits (10) and the third one is a multiplier (2=100 as per table);
and, alphabet represent tolerance (K= 10%) value as shown in the figure.
Capacitor Number Coding
Some more methods of
finding the capacitor values include the following
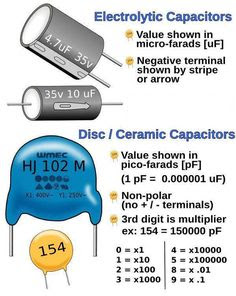
1. The number printed
on the capacitor’s body represents the capacitance value in Pico Farads.
For example, 8 = 8PF
2. If the third number
is zero, then the value is in Picofarad
For example, 100 = 100PF
3. For a 3-digit
value, the third digit represents the number of zeros after the second digit
For example, 104 = 10 – 0000 PF
4. If the value
is obtained in PF, then it is easy to convert it into KPF or uF
For example, PF / 1000 = KPF or, PF / 10, 00000 = uF. For a
capacitance value of 104 or 100000 in pF, it is 100KpF or n or 0.1uF.
5. For a 4-digit
number, if the 4th number is a zero, then the capacitance
value is in pF.
E.g. 1500 = 1500PF
6. If the number is a
floating point decimal number, then the capacitance value is in uF.
E.g. 0.1 = 0.1 uF
7. If an alphabet is
given between the digits, it represents a decimal and the value is in KPF
E.g. 2K2 = 2.2 KPF
8. If the values are
represented with slashes, then the first digit represents value in UF, the second
digit gives tolerance and the third represents maximum voltage rating.
E.g. 0.1/5/800 = 0.01 uF / 5 % / 800 Volt.
Capacitor Color Coding Value Calculator Chart
The first color is considered as the 1st digit in color chart, the second color band is 2nd digit, the third band is a multiplier, the 4th band is tolerance and the fifth color band is voltage rating of the capacitor. The capacitor color code chart is given below to identify the value of the capacitor
For example, consider the below capacitor wherein each color is
represented with some value. The first band is orange that has value of 3 in
the above chart, the second band is yellow 4, and the third one is 0.1
multiplier and the fourth band red is 0.25 tolerance.
Then its value is 34*0.1 pF with a tolerance of 0.25; finally,
it is 3.4pF with a tolerance of 0.25 as shown in the figure.



What is Capacitor?
Capacitor is a passive element that stores electric charge statistically and temporarily as an static electric field. It is composed of two parallel conducting plates separated by non-conducting region that is called dielectric, such as vacuum, ceramic, air, aluminum, etc.
The capacitance formula of the capacitor is represented by,
The capacitance formula of the capacitor is represented by,

C is the capacitance that is proportional to the area of the two conducting plates (A) and proportional with the permittivity ε of the dielectric medium. The capacitance decreases with the distance between plates (d). We get the greatest capacitance with a large area of plates separated by a small distance and located in a high permittivity material. The standard unit of capacitance is Farad, most commonly it can be found in micro-farads, pico-farads and nano-farads.
General uses of Capacitors
- Smoothing, especially in power supply applications which required converting the signal from AC to DC.
- Smoothing, especially in power supply applications which required converting the signal from AC to DC.
- Storing Energy.
- Storing Energy.
- Signal decoupling and coupling as a capacitor coupling that blocks DC current and allow AC current to pass in circuits.
- Signal decoupling and coupling as a capacitor coupling that blocks DC current and allow AC current to pass in circuits.
- Tuning, as in radio systems by connecting them to LC oscillator and for tuning to the desired frequency.
- Tuning, as in radio systems by connecting them to LC oscillator and for tuning to the desired frequency.
- Timing, due to the fixed charging and discharging time of capacitors.
- Timing, due to the fixed charging and discharging time of capacitors.
- For electrical power factor correction and many more applications.
- For electrical power factor correction and many more applications.
Charging a Capacitor
Capacitors are mainly categorized on the basis of dielectric used in them. During choosing a specific type of capacitors for a specific application, there are numbers of factors that get considered. The value of capacitance is one of the vital factors to be considered. Not only this, many other factors like, operating voltage, allowable tolerance stability, leakage
resistance, size and prices are also very important factors to be considered during choosing specific type of capacitors.

Hence, it is cleared that, by varying ε, A or d we can easily change the value of C. If we require higher value of capacitance (C) we have to increase the cross-sectional area of dielectric or we have to reduce the distance of separation or we have to use dielectric material with stronger permittivity.
Types of Capacitors
The various types of capacitors have been developed to overcome these problems in a number of ways.
Paper Capacitor
It is one of the simple forms of capacitors. Here, a waxed paper is sandwiched between two aluminium foils.
Process of making this capacitor is quite simple. Take place of aluminium foil. Cover this foil with a waxed paper. Now, cover this waxed paper with another aluminium foil. Then roll up this whole thing as a cylinder. Put two metal caps at both ends of roll. This whole assembly is then encapsulated in a case. By rolling up, we make quite a large cross-sectional area of capacitor assembled in a reasonably smaller space.
We know that capacitance of a capacitor is given by,
If we go only for the increasing area of cross-section, the rise of the capacitor may become quite large; which may not be practically acceptable. Again if we reduce only the distance of separation, the thickness of dielectric becomes very thin. But the dielectric cannot be made too thin in case its dielectric strength in exceeded.
Air Capacitor
There are two sets of parallel plates. One set of plates is fixed and another set of plates is movable. When the knob connected with the capacitor is rotated, the movable set of plates rotates and overlapping area as between fixed and movable plates vary. This causes variation in effective cross-sectional areas of the capacitor. Consequently, the capacitance varies when one rotates the knob attached to the air capacitor. This type of capacitor is generally used to tune the bandwidth of a radio receiver.

Plastic Capacitor
When various plastic materials are used as dielectric material, the capacitors are said to be plastic capacitors. The plastic material may be of polyester, polystyrene, polycarbonate or poly propylene. Each of these materials has slightly different electrical characteristics, which can be used to advantage, depending upon the proposed application.
This type of capacitors is constructional, more or less same as paper capacitor. That means, a thin sheet one of the earlier mentioned plastic dielectrics, is kept between two aluminium foils. That means, here the flexible thin plastic sheet is used as dielectric instead of waxed paper. Here, the plastic sheet covered by aluminium foil from two sides, is first rolled up, then fitted with metal end caps, and then the whole assembly is encapsulated in a case.
Plastic Film Capacitor
Plastic capacitor can be made also in form of film capacitor. Here, thin strips or films of plastic are kept inside metallic strips. Each metallic strip is connected to side metallic contact layer alternatively; as shown in the figure below. That means, if one metallic strip is connected to left side contact layer, then the very next is connected to right side contact layer. And there are plastic films in between these metallic strips. The terminals of this type of capacitors are also connected to side contact layer and whole assembly is covered with insulated non metallic cover as shown.

Silvered Mica Capacitor
A silvered mica capacitor is very accurate and reliable capacitor. This type of capacitors has very low tolerance. But on the other hand, cost of this capacitor is quite higher compared to other available capacitors in the market. But this high cost capacitor can easily be compensated by its high quality and performance. A small ceramic disc or cylinder is coated by silver compound. Here, electrical terminal is affixed on the silver coating and the whole assembly is encapsulated in a casing.
Ceramic Capacitor
Construction of ceramic capacitor is quite simple. Here, one thin ceramic disc is placed between two metal discs and terminals are soldered to the metal discs. Whole assembly is coated with insulated protection coating as shown in the figure below.

Mixed Dielectric Capacitor
The way of constructing this capacitor is same as paper capacitor. Here, instead of moving waxed paper as dielectric, paper impregnated with polyester is used as dielectric between two conductive aluminium foils.
Electrolyte Capacitor
Very large value of capacitance can be achieved by this type of capacitor. But working voltage level of this electrolyte capacitor is low and it also suffers from high leakage current. The main disadvantage of this capacitor is that, due to the use of electrolyte, the capacitor is polarized. The polarities are marked against the terminals with + and – sign and the capacitor must be connected to the circuit in proper polarity.
A few micro meter thick aluminium oxide or tantalum oxide film is used as dielectric of electrolyte capacitor. As this dielectric is so thin, the capacitance of this type of capacitor is very high. This is because; the capacitance is inversely proportional to thickness of the dielectric. Thin dielectric obviously increases the capacitance value but at the same time, it reduces working voltage of the device. Tantalum type capacitors are usually much smaller in size than the aluminium type capacitors of same capacitance value. That is why, for very high value of capacitance, aluminium type electrolyte capacitors do not get used generally. In that case, tantalum type electrolyte capacitors get used.
Aluminium electrolyte capacitor is formed by a paper impregnated with an electrolyte and two sheets of aluminium. These two sheets of aluminium are separated by the paper impregnated with electrolyte. The whole assembly is then rolled up in a cylindrical form, just like a simple paper capacitor. This roll is then placed inside a hermetically sealed aluminium canister. The oxide layer is formed by passing a charging current through the device, and it is the polarity of this charging process that determines the resulting terminal polarity that must be subsequently observed. If the opposite polarity is applied to the capacitor, the oxide layer is destroyed.
| Material | Dielectric constant | Dielectric Strength Volts/.001 inch |
| Air | 1 | 80 |
| Paper(Oiled) | 3-4 | 1500 |
| Mica | 4-8 | 1800 |
| Glass | 4-8 | 200 |
| Porcelain | 5 | 750 |
| Titanates | 100-200 | 100 |